Posted: 2013/07/17 | Author: amarashiki | Filed under: Basic Neutrinology, Physmatics, The Standard Model: Basics | Tags: 5 sigma, CMB, CNB, cosmic ray, cosmic rays and physics, cross-section, delta particle, delta resonance, Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin limit, GZK cut-off, GZK effect, H-burst, H-dip, neutrino astronomy, neutrino cosmology, neutrino spectroscopy, neutrinology, resonance, X-burst, X-dip, Z-burst, Z-dip, Zetta-electron-volt, ZeV, Zevatron |

The topic today is a fascinant subject in Neutrino Astronomy/Astrophysics/Cosmology. I have talked you in this thread about the cosmic neutrino background ( ) and that the young neutrino Astronomy or neutrino telescopes will become more and more important in the future. The reasons are simple:
) and that the young neutrino Astronomy or neutrino telescopes will become more and more important in the future. The reasons are simple:
1st. If we want to study the early Universe, we need some “new” tool to overcome the last scattering surface as a consequence of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Neutrinos are such a new tool/probe! They only interact weakly with matter and we suspect that there are some important pieces of information related to the quark and lepton “complementarity” hidden in their mixing parameters.
2nd. Due to the GZK effect, we expect that the flux of cosmic rays will suffer a sudden cut-off at about 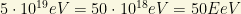 , or about 8 joules. This Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin limit (GZK limit) is a theoretical upper limit on the energy of cosmic rays, since at some high energy, that can be computed, they would interact with the CMB photons producing a delta particle (
, or about 8 joules. This Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin limit (GZK limit) is a theoretical upper limit on the energy of cosmic rays, since at some high energy, that can be computed, they would interact with the CMB photons producing a delta particle ( ) which would spoil the observed cosmic rays flux as its decays would not be detected after “a long trip”. Then, it can only be approached when the cosmic rays travel very long distances (hundreds of million light-years or more). Here you are a typical picture of SuperKamiokande cosmic ray detection:
) which would spoil the observed cosmic rays flux as its decays would not be detected after “a long trip”. Then, it can only be approached when the cosmic rays travel very long distances (hundreds of million light-years or more). Here you are a typical picture of SuperKamiokande cosmic ray detection:

The limit is at the same order of magnitude as the upper limit for energy at which cosmic rays have experimentally been detected. There are some current experiments that “claim” to have observed this GZK effect, but evidence is not conclusive yet as far as I know. Some experiments claim (circa 2013, July) to have observed it, other experiments claim to have observed events well above the GZK limit. The next generation of cosmic ray experiments will confirm this limit from SM physics or they will show us interesting new physics events!
Inspired by the GZK effect, some people have suggested an indirect way to detect the existence of the cosmic relic neutrinos. Remember, cosmic neutrinos have a temperature about  if the SM is right, and their associated neutrino density now is about
if the SM is right, and their associated neutrino density now is about  per cubic centimeter per species (neutrino plus antineutrino), or
per cubic centimeter per species (neutrino plus antineutrino), or  per cubic centimeter including the 3 flavors! Relic neutrinos are almost everywhere, but they are very, very feeble (neutral and weakly interacting) particles. While detecting the
per cubic centimeter including the 3 flavors! Relic neutrinos are almost everywhere, but they are very, very feeble (neutral and weakly interacting) particles. While detecting the  temperature is one of the most challenging tests of the standard cosmological model, we can try to detect the existence of these phantom neutrinos using a similar (quantum) trick than the one used in the GZK limit (there the delta particle resonance). If some ultra high energy cosmic ray (likely a neutrino coming from some astrophysical source) hits a “relic neutrino” with energy high enough to produce, say, a Z boson (neutral particle as the neutrino himself), then we should observe a “dip” in the cosmic ray spectrum corresponding to this “Z-burst” event! This mechanism is also called the ZeVatron or the Z-dip. It also shows the deep links between particle physics and Cosmology or Astrophysics. When an ultra-high energy cosmic neutrino collides with a relic anti-neutrino in our galaxy and annihilates to hadrons, this process proceeds via a (virtual) Z-boson:
temperature is one of the most challenging tests of the standard cosmological model, we can try to detect the existence of these phantom neutrinos using a similar (quantum) trick than the one used in the GZK limit (there the delta particle resonance). If some ultra high energy cosmic ray (likely a neutrino coming from some astrophysical source) hits a “relic neutrino” with energy high enough to produce, say, a Z boson (neutral particle as the neutrino himself), then we should observe a “dip” in the cosmic ray spectrum corresponding to this “Z-burst” event! This mechanism is also called the ZeVatron or the Z-dip. It also shows the deep links between particle physics and Cosmology or Astrophysics. When an ultra-high energy cosmic neutrino collides with a relic anti-neutrino in our galaxy and annihilates to hadrons, this process proceeds via a (virtual) Z-boson:
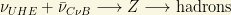

The cross section for this process becomes large if the center of mass energy of the neutrino-antineutrino pair is equal to the Z-boson mass (such a peak in the cross section is what we call “resonance” in High Energy physics). Assuming that the relic anti-neutrino is at rest, the energy of the incident cosmic neutrino has to be the quantity:
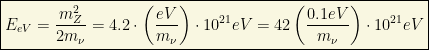
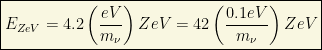

In fact, this mechanism based on “neutral resonances” is completely “universal”! Nothing (except some hidden symmetry or similar) can allow the production of (neutral) particles using this cosmic method. For instance, if this argument is true, beyond the Z-burst, we should be able to detect Higgs-dips (Higgs-bursts) or H-dips, since, similarely we could have
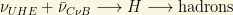
or more generally, with some (likely) “dark” particle, we should also expect that

In the H-dip case, taking the measured Higgs mass from the last LHC run (about 126GeV), we get


In the arbitrary “dark” or “weakly interacting” particle, we have (in general, with  ) the formulae:
) the formulae:
or equivalently
Therefore, cosmic ray neutrino spectroscopy is a very interesting subject yet to come! It can provide:
1st. Evidences for relic neutrinos we expect from the standard cosmological model.
2nd. Evidence for the Higgs boson in astrophysical scenarios from cosmological neutrinos. Now, we know that the Higgs field and the Higgs particle do exist, so it is natural to seek out this H-dips as well!
3rd. Evidence for the additional neutral weakly interacting (and/or “dark”) particles from “unexpected” dips at ZeV (1ZeV=1Zetta electron-volt) or even higher energies! Of course, this is the most interesting part from the viewpoint of new physics searches!
Neutrino telescopes and their associated Astronomy is just rising now! IceCube is its most prominent example…
Moreover, following one of the most interesting things in any research (expect the unexpected and try to explain it!) from the scientific viewpoint, I am quite sure the neutrino astronomy and its interplay with cosmic rays or this class of “neutrino spectroscopy” in the flux of cosmic rays open a very interesting window for the upcoming new physics. Are we ready for it? Maybe…After all, the neutrino mixing parameters are very different (“complementary”?) to the quark mixing parameters. You can observe it in this mass-flavor content plot:
 Neutrino oscillations are a purely quantum effect, and thus, they open a really interesting “new channel” in which we can observe the whole Universe. Yes, neutrinos are cool!!! The coolest particles in all over the world! We can not imagine yet what neutrino will show and teach us about the current, past and future of the cosmological evolution.
Neutrino oscillations are a purely quantum effect, and thus, they open a really interesting “new channel” in which we can observe the whole Universe. Yes, neutrinos are cool!!! The coolest particles in all over the world! We can not imagine yet what neutrino will show and teach us about the current, past and future of the cosmological evolution.

Remark: When I saw the Fermi line and the claim of the Dark Matter particle “evidence” at about 130 GeV, I wondered if it could be, indeed, a hint of a similar “resonant” process in gamma rays, something like

since the line “peaked” close to the known Higgs-like particle mass ( ). Anyway, this line is controversial and its presence has yet to be proved with enough statistical confidence (5 sigmas are usually required in the particle physics community). Of course, the issue with this resonant hypothesis would be that we should expect that this particle would decay into hadrons leaving some indirect clues of those events. The Fermi line can indeed have more explanations and/or be a fluke in the data due to a bad modeling or a bad substraction of the background. Time will tell us if the Fermi line is really here as well.
). Anyway, this line is controversial and its presence has yet to be proved with enough statistical confidence (5 sigmas are usually required in the particle physics community). Of course, the issue with this resonant hypothesis would be that we should expect that this particle would decay into hadrons leaving some indirect clues of those events. The Fermi line can indeed have more explanations and/or be a fluke in the data due to a bad modeling or a bad substraction of the background. Time will tell us if the Fermi line is really here as well.
Final (geek) remark: I wonder if the Doctor Who fans remember that the reality bomb of Davros and the Daleks used “Z-neutrinos“!!! I presently do not know if the people who wrote those scripts and imagined the Z-neutrino were aware of the Z-bursts…Or not… LOL The Z-neutrino powered crucible was really interesting…

And the reality bomb concept was really scaring…

However, neutrinos are pretty weakly interacting particles, at least when they have low energy, so we should have not fear them. After all, their future applications will surprise us much more. I am quite sure of it!
See you in my next neutrinological post!
May the Z(X)-burst induced superGZK neutrinos be with you!
claimtoken-51ead3d045a40
Posted: 2013/07/15 | Author: amarashiki | Filed under: Basic Neutrinology, Physmatics, The Standard Model: Basics | Tags: CDM, CMB, CNB, cold dark matter, cosmic neutrino background, cosmological constant, critical density, HDM, hot dark matter, matter density, neutrino astronomy, neutrino comoslogy, neutrino decoupling, neutrino mass bounds from cosmology, neutrinology, number of effective neutrino species, PLANCK, total matter density, Tremaine-Gunn limit, WMAP |
There are some indirect constraints/bounds on neutrino masses provided by Cosmology. The most important is the one coming from the demand that the energy density of the neutrinos should not be too high, otherwise the Universe would collapse and it does not happen, apparently…
Firstly, stable neutrinos with low masses (about  ) make a contribution to the total energy density of the Universe given by:
) make a contribution to the total energy density of the Universe given by:

and where the total mass is defined to be the quantity

Here, the number of degrees of freedom  for Dirac (Majorana) neutrinos in the framework of the Standard Model. The number density of the neutrino sea is revealed to be related to the photon number density by entropy conservation (entropy conservation is the key of this important cosmological result!) in the adiabatic expansion of the Universe:
for Dirac (Majorana) neutrinos in the framework of the Standard Model. The number density of the neutrino sea is revealed to be related to the photon number density by entropy conservation (entropy conservation is the key of this important cosmological result!) in the adiabatic expansion of the Universe:
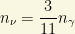
From this, we can derive the relationship of the cosmic relic neutrino background (neutrinos coming from the Big Bang radiation when they lost the thermal equilibrium with photons!) or  and the cosmic microwave background (CMB):
and the cosmic microwave background (CMB):
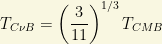
From the CMB radiation measurements we can obtain the value
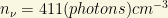
for a perfect Planck blackbody spectrum with temperature

This CMB temperature implies that the  temperature should be about
temperature should be about

Remark: if you do change the number of neutrino degrees of freedom you also change the temperature of the  and the quantity of neutrino “hot dark matter” present in the Universe!
and the quantity of neutrino “hot dark matter” present in the Universe!
Moreover, the neutrino density  is related to the total neutrino density and the critical density as follows:
is related to the total neutrino density and the critical density as follows:
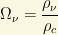
and where the critical density is about
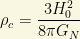
When neutrinos “decouple” from the primordial plasma and they loose the thermal equilibrium, we have  , and then we get
, and then we get
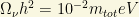
with 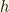 the reduced Hubble constant. Recent analysis provide
the reduced Hubble constant. Recent analysis provide 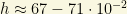 (PLANCK/WMAP).
(PLANCK/WMAP).
There is another useful requirement for the neutrino density in Cosmology. It comes from the requirements of the BBN (Big Bang Nucleosynthesis). I talked about this in my Cosmology thread. Galactic structure and large scale observations also increase evidence that the matter density is:

These values are obtained through the use of the luminosity-density relations, galactic rotation curves and the observation of large scale flows. Here, the  is the total mass density of the Universe as a fraction of the critical density
is the total mass density of the Universe as a fraction of the critical density 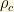 . This
. This  includes radiation (photons), bayrons and non-baryonic “cold dark matter” (CDM) and “hot dark matter” (HDM). The two first components in the decomposition of
includes radiation (photons), bayrons and non-baryonic “cold dark matter” (CDM) and “hot dark matter” (HDM). The two first components in the decomposition of 
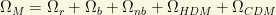
are rather well known. The photon density is

The deuterium abundance can be extracted from the BBN predictions and compared with the deuterium abundances in the stellar medium (i.e. at stars!). It shows that:
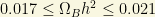
The HDM component is formed by relativistic long-lived particles with masses less than about 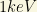 . In the SM framework, the only HDM component are the neutrinos!
. In the SM framework, the only HDM component are the neutrinos!
The simulations of structure formation made with (super)computers fit the observations ONLY when one has about 20% of HDM plus 80% of CDM. A stunning surprise certainly! Some of the best fits correspond to neutrinos with a total mass about 4.7eV, well above the current limit of neutrino mass bounds. We can evade this apparent contradiction if we suppose that there are some sterile neutrinos out there. However, the last cosmological data by PLANCK have decreased the enthusiasm by this alternative. The apparent conflict between theoretical cosmology and observational cosmology can be caused by both unprecise measurements or our misunderstanding of fundamental particle physics. Anyway observations of distant objects (with high redshift) favor a large cosmological constant instead of Hot Dark Matter hypothesis. Therefore, we are forced to conclude that the HDM of  does not exceed even
does not exceed even 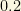 . Requiring that
. Requiring that 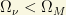 , we get that
, we get that  . Using the relationship with the total mass density, we can deduce that the total neutrino mass (or HDM in the SM) is about
. Using the relationship with the total mass density, we can deduce that the total neutrino mass (or HDM in the SM) is about
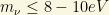 or less!
or less!
Mass limits, in this case lower limits, for heavy or superheavy neutrinos ( or higher) can also be obtained along the same reasoning. The puzzle gets very different if the neutrinos were “unstable” particles. One gets then joint bounds on mass and timelife, and from them, we deduce limits that can overcome the previously seen limits (above).
or higher) can also be obtained along the same reasoning. The puzzle gets very different if the neutrinos were “unstable” particles. One gets then joint bounds on mass and timelife, and from them, we deduce limits that can overcome the previously seen limits (above).
There is another interesting limit to the density of neutrinos (or weakly interacting dark matter in general) that comes from the amount of accumulated “density” in the halos of astronomical objects. This is called the Tremaine-Gunn limit. Up to numerical prefactors, and with the simplest case where the halo is a singular isothermal sphere with  , the reader can easily check that
, the reader can easily check that
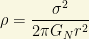
Imposing the phase space bound at radius r then gives the lower bound

This bound yields 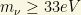 . This is the Tremaine-Gunn bound. It is based on the idea that neutrinos form an important part of the galactic bulges and it uses the phase-space restriction from the Fermi-Dirac distribution to get the lower limit on the neutrino mass. I urge you to consult the literature or google to gather more information about this tool and its reliability.
. This is the Tremaine-Gunn bound. It is based on the idea that neutrinos form an important part of the galactic bulges and it uses the phase-space restriction from the Fermi-Dirac distribution to get the lower limit on the neutrino mass. I urge you to consult the literature or google to gather more information about this tool and its reliability.
Remark: The singular isothermal sphere is probably a good model where the rotation curve produced by the dark matter halo is flat, but certainly breaks down at small radius. Because the neutrino mass bound is stronger for smaller 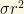 , the uncertainty in the halo core radius (interior to which the mass density saturates) limits the reliability of this neutrino mass bound. However, some authors take it seriously! As Feynman used to say, everything depends on the prejudges you have!
, the uncertainty in the halo core radius (interior to which the mass density saturates) limits the reliability of this neutrino mass bound. However, some authors take it seriously! As Feynman used to say, everything depends on the prejudges you have!
The abundance of additional weakly interacting light particles, such as a light sterile neutrino 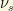 or additional relativistic degrees of freedom uncharged under the Standard Model can change the number of relativistic degrees of freedom
or additional relativistic degrees of freedom uncharged under the Standard Model can change the number of relativistic degrees of freedom  . Sometimes you will hear about the number
. Sometimes you will hear about the number  . Planck data, recently released, have decreased the hopes than we would be finding some additional relativistic degree of freedom that could mimic neutrinos. It is also constrained by the BBN and the deuterium abundances we measured from astrophysical objects. Any sterile neutrino or extra relativistic degree of freedom would enter into equilibrium with the active neutrinos via neutrino oscillations! A limit on the mass differences and mixing angle with another active neutrino of the type
. Planck data, recently released, have decreased the hopes than we would be finding some additional relativistic degree of freedom that could mimic neutrinos. It is also constrained by the BBN and the deuterium abundances we measured from astrophysical objects. Any sterile neutrino or extra relativistic degree of freedom would enter into equilibrium with the active neutrinos via neutrino oscillations! A limit on the mass differences and mixing angle with another active neutrino of the type
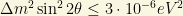 should be accomplished in principle. From here, it can be deduced that the effective number of neutrino species allowed by neutrino oscillations is in fact a litle higher the the 3 light neutrinos we know from the Z-width bound:
should be accomplished in principle. From here, it can be deduced that the effective number of neutrino species allowed by neutrino oscillations is in fact a litle higher the the 3 light neutrinos we know from the Z-width bound:

PLANCK data suggest indeed that 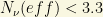 . However, systematical uncertainties in the derivation of the BBN make it too unreliable to be taken too seriously and it can eventually be avoided with care.
. However, systematical uncertainties in the derivation of the BBN make it too unreliable to be taken too seriously and it can eventually be avoided with care.
Posted: 2013/07/13 | Author: amarashiki | Filed under: Basic Neutrinology, Physmatics, The Standard Model: Basics | Tags: AGN, Astrophysics, atmospheric neutrinos, baryogenesis, CMB, CNB, cosmic diffuse neutrino background, cosmic neutrino background, cosmic rays, cosmological models, Cosmology, CP violation, Dirac neutrino, DONUT, double beta decay, E.Fermi, electron, electroweak scale, flavor, gravity, HDM, hot dark matter (HDM), IceCube, inverted hierarchy, KamLAND, leptogenesis, leptons, long baseline experiments, majorana neutrino, massive neutrinos, MINOS, muon, neutrino flavor, neutrino mass, neutrino mass bounds, neutrino mixing, neutrino oscillations, neutrino species, neutrinoless double beta decay, neutrinology, New Physics, NO, NOCILLA, normal hierarchy, NOSEX, quasidegenerated neutrino spectrum, reactor experiment, reactor neutrinos, Reines-Cowan experiment, relic cosmic neutrinos, seesaw, short baseline experiments, SM fermions, SNO, solar neutrino problem, solar neutrinos, Standard Model, Stantadard Cosmological Model, sterile neutrinos, SuperKamiokande, tau particle, W. Pauli, weak interactions |


This new post ignites a new thread.
Subject: the Science of Neutrinos. Something I usually call Neutrinology.
I am sure you will enjoy it, since I will keep it elementary (even if I discuss some more advanced topics at some moments). Personally, I believe that the neutrinos are the coolest particles in the Standard Model, and their applications in Science (Physics and related areas) or even Technology in the future ( I will share my thoughts on this issue in a forthcoming post) will be even greater than those we have at current time.
Let me begin…
The existence of the phantasmagoric neutrinos ( light, electrically neutral and feebly -very weakly- interacting fermions) was first proposed by W. Pauli in 1930 to save the principle of energy conservation in the theory of nuclear beta decay. The idea was promptly adopted by the physics community but the detection of that particle remained elusive: how could we detect a particle that is electrically neutral and that interact very,very weakly with normal matter? In 1933, E. Fermi takes the neutrino hypothesis, gives the neutrino its name (meaning “little neutron”, since it was realized than neutrinos were not Chadwick’s neutrons) and builds his theory of beta decay and weak interactions. With respect to its mass, Pauli initially expected the mass of the neutrino to be small, but necessarily zero. Pauli believed (originally) that the neutrino should not be much more massive than the electron itself. In 1934, F. Perrin showed that its mass had to be less than that of the electron.
By the other hand, it was firstly proposed to detect neutrinos exploding nuclear bombs! However, it was only in 1956 that C. Cowan and F. Reines (in what today is known as the Reines-Cowan experiment) were able to detect and discover the neutrino (or more precisely, the antineutrino). In 1962, Leon M. Lederman, M. Schwartz, J. Steinberger and Danby et al. showed that more than one type of neutrino species  should exist by first detecting interactions of the muon neutrino. They won the Nobel Prize in 1988.
should exist by first detecting interactions of the muon neutrino. They won the Nobel Prize in 1988.
When we discovered the third lepton, the tau particle (or tauon), in 1975 at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, it too was expected to have an associated neutrino particle. The first evidence for this 3rd neutrino “flavor” came from the observation of missing energy and momentum in tau decays. These decays were analogue to the beta decay behaviour leading to the discovery of the neutrino particle.
In 1989, the study of the Z boson lifetime allows us to show with great experimental confidence that only 3 light neutrino species (or flavors) do exist. In 2000, the first detection of tau neutrino ( in addition to
in addition to  ) interactions was announced by the DONUT collaboration at Fermilab, making it the latest particle of the Standard Model to have been discovered until the recent Higgs particle discovery (circa 2012, about one year ago).
) interactions was announced by the DONUT collaboration at Fermilab, making it the latest particle of the Standard Model to have been discovered until the recent Higgs particle discovery (circa 2012, about one year ago).
In 1998, research results at the Super-Kamiokande neutrino detector in Japan (and later, independently, from SNO, Canada) determined for the first time that neutrinos do indeed experiment “neutrino oscillations” (I usually call NOCILLA, or NO for short, this phenomenon), i.e., neutrinos flavor “oscillate” and change their flavor when they travel “short/long” distances. SNO and Super-Kamiokande tested and confirmed this hypothesis using “solar neutrinos”. this (quantum) phenomenon implies that:
1st. Neutrinos do have a mass. If they were massless, they could not oscillate. Then, the old debate of massless vs. massive neutrinos was finally ended.


2nd. The solar neutrino problem is solved. Some solar neutrinos scape to the detection in Super-Kamiokande and SNO, since they could not detect all the neutrino species. It also solved the old issue of “solar neutrinos”. The flux of (detected) solar neutrinos was lesser than expected (generally speaking by a factor 2). The neutrino oscillation hypothesis solved it since it was imply the fact that some neutrinos have been “transformed” into a type we can not detect.

3rd. New physics does exist. There is new physics at some energy scale beyond the electroweak scale (the electroweak symmetry breaking and typical energy scale is about 100GeV). The SM is not complete. The SM does (indeed) “predict” that the neutrinos are massless. Or, at least, it can be made simpler if you make neutrinos to be massless neutrinos described by Weyl spinors. It shows that, after the discovery of neutrino oscillations, it is not the case. Neutrinos are massive particles. However, they could be Dirac spinors (as all the known spinors in the Standard Model, SM) or they could also be Majorana particles, neutral fermions described by “Majorana” spinors and that makes them to be their own antiparticles! Dirac particles are different to their antiparticles. Majorana particles ARE the same that their own antiparticles.

In the period 2001-2005, neutrino oscillations (NO)/neutrino mixing phenomena(NEMIX) were observed for the first time at a reactor experiment (this type of experiment are usually referred as short baseline experiment in the neutrino community) called KamLAND. They give a good estimate (by the first time) of the difference in the squares of the neutrino masses. In May 2010, it was reported that physicists from CERN and the Italian National Institute for Nuclear Physics, in Gran Sasso National Laboratory, had observed for the first time a transformation between neutrino flavors during an accelerator experiment (also called neutrino beam experiment, a class of neutrino experiment belonging to “long range” or “long” baseline experiments with neutrino particles). It was a new solid evidence that at least one neutrino species or flavor does have mass. In 2012, the Daya Bay Reactor experiment in China, and later RENO in South Korea measured the so called  mixing angle, the last neutrino mixing angle remained to be measured from the neutrino mass matrix. It showed to be larger than expected and it was consistent with earlier, but less significant results by the experiments T2K (another neutrino beam experiment), MINOS (other neutrino beam experiment) and Double Chooz (a reactor neutrino experiment).
mixing angle, the last neutrino mixing angle remained to be measured from the neutrino mass matrix. It showed to be larger than expected and it was consistent with earlier, but less significant results by the experiments T2K (another neutrino beam experiment), MINOS (other neutrino beam experiment) and Double Chooz (a reactor neutrino experiment).
With the known value of  there are some probabilities that the
there are some probabilities that the 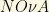 experiment at USA can find the neutrino mass hierarchy. In fact, beyond to determine the spinorial character (Dirac or Majorana) of the neutrino particles, and to determine their masses (yeah, we have not been able to “weight” the neutrinos, but we are close to it: they are the only particle in the SM with no “precise” value of mass), the remaining problem with neutrinos is to determine what kind of spectrum they have and to measure the so called CP violating processes. There are generally 3 types of neutrino spectra usually discussed in the literature:
experiment at USA can find the neutrino mass hierarchy. In fact, beyond to determine the spinorial character (Dirac or Majorana) of the neutrino particles, and to determine their masses (yeah, we have not been able to “weight” the neutrinos, but we are close to it: they are the only particle in the SM with no “precise” value of mass), the remaining problem with neutrinos is to determine what kind of spectrum they have and to measure the so called CP violating processes. There are generally 3 types of neutrino spectra usually discussed in the literature:
A) Normal Hierarchy (NH):  . This spectrum follows the same pattern in the observed charged leptons, i.e.,
. This spectrum follows the same pattern in the observed charged leptons, i.e.,  . The electron is about 0.511MeV, muon is about 106 MeV and the tau particle is 1777MeV.
. The electron is about 0.511MeV, muon is about 106 MeV and the tau particle is 1777MeV.
B) Inverted Hierarchy (IH):  . This spectrum follows a pattern similar to the electron shells in atoms. Every “new” shell is closer in energy (“mass”) to the previous “level”.
. This spectrum follows a pattern similar to the electron shells in atoms. Every “new” shell is closer in energy (“mass”) to the previous “level”.
C) Quasidegenerated (or degenerated) hierarchy/spectrum (QD):  .
.


While the above experiments show that neutrinos do have mass, the absolute neutrino mass scale is still not known. There are reasons to believe that its mass scale is in the range of some milielectron-volts (meV) up to the electron-volt scale (eV) if some extra neutrino degree of freedom (sterile neutrinos) do appear. In fact, the Neutrino OScillation EXperiments (NOSEX) are sensitive only to the difference in the square of the neutrino masses. There are some strongest upper limits on the masses of neutrinos that come from Cosmology:
1) The Big Bang model states that there is a fixed ratio between the number of neutrino species and the number of photons in the cosmic microwave background (CMB). If the total energy of all the neutrino species exceeded an upper bound about
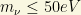
per neutrino, then, there would be so much mass in the Universe that it would collapse. It does not (apparently) happen.
2) Cosmological data, such as the cosmic microwave background radiation, the galaxy surveys, or the technique of the Lyman-alpha forest indicate that the sum of the neutrino masses should be less than 0.3 eV (if we don’t include sterile neutrinos, new neutrino species uncharged under the SM gauge group, that could increase that upper bound a little bit).
3) Some early measurements coming from lensing data of a galaxy cluster were analyzed in 2009. They suggest that the neutrino mass upper bound is about 1.5eV. This result is compatible with all the above results.
Today, some measurements in controlled experiments have given us some data about the squared mass differences (from both, solar neutrinos, atmospheric neutrinos produced by cosmic rays and accelerator/reactor experiments):
1) From KamLAND (2005), we get
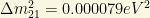
2) From MINOS (2006), we get
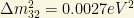
There are some increasing efforts to directly determine the absolute neutrino mass scale in different laboratory experiments (LEX), mainly:
1) Nuclear beta decay (KATRIN, MARE,…).
2) Neutrinoless double beta decay (e.g., GERDA; CUORE, Cuoricino, NEMO3,…). If the neutrino is a Majorana particle, a new kind of beta decay becomes possible: the double beta decay without neutrinos (i.e., two electrons emitted and no neutrino after this kind of decay).
Neutrinos have a unique place among all the SM elementary particles. Their role in the cosmic evolution and the fundamental asymmetries in the SM (like CP violating reactions, or the C, T, and P single violations) make them the most fascinating and interesting particle that we know today (well, maybe, today, the Higgs particle is also as mysterious as the neutrino itself). We believe that neutrinos play an important role in Beyond Standard Model (BSM) Physics. Specially, I would like to highlight two aspects:
1) Baryogenesis from leptogenesis. Neutrinos can allow us to understand how could the Universe end in such an state that it contains (essentially) baryons and no antibaryons (i.e., the apparent matter-antimatter asymmetry of the Universe can be “explained”, with some unsolved problems we have not completely understood, if massive neutrinos are present).
2) Asymmetric mass generation mechanisms or the seesaw. Neutrinos allow us to build an asymmetric mass mechanism known as “seesaw” that makes “some neutrino species/states” very light and other states become “superheavy”. This mechanism is unique and, from some non-subjective viewpoint, “simple”.
After nearly a century, the question of the neutrino mass and its origin is still an open question and a hot topic in high energy physics, particle physics, astrophysics, cosmology and theoretical physics in general.
If we want to understand the fermion masses, a detailed determination of the neutrino mass is necessary. The question why the neutrino masses are much smaller than their charged partners could be important! The little hierarchy problem is the problem of why the neutrino mass scale is smaller than the other fermionic masses and the electroweak scale. Moreover, neutrinos are a powerful probe of new physics at scales larger than the electroweak scale. Why? It is simple. (Massive) Neutrinos only interact under weak interactions and gravity! At least from the SM perspective, neutrinos are uncharged under electromagnetism or the color group, so they can only interact via intermediate weak bosons AND gravity (via the undiscovered gravitons!).
If neutrino are massive particles, as they show to be with the neutrino oscillation phenomena, the superposition postulates of quantum theory state that neutrinos, particles with identical quantum numbers, could oscillate in flavor space since they are electrically neutral particles. If the absolute difference of masses among them is small, then these oscillations or neutrino (flavor) mixing could have important phenomenological consequences in Astrophysics or Cosmology. Furthermore, neutrinos are basic ingredients of these two fields (Astrophysics and Cosmology). There may be a hot dark matter component (HDM) in the Universe: simulations of structure formation fit the observations only when some significant quantity of HDM is included. If so, neutrinos would be there, at least by weight, and they would be one of the most important ingredients in the composition of the Universe.


Regardless the issue of mass and neutrino oscillations/mixing, astrophysical interests in the neutrino interactions and their properties arise from the fact that it is produced in high temperature/high density environment, such as collapsing stars and/or supernovae or related physical processes. Neutrino physics dominates the physics of those astrophysical objects. Indeed, the neutrino interactions with matter is so weak, that it passes generally unnoticed and travels freely through any ordinary matter existing in the Universe. Thus, neutrinos can travel millions of light years before they interact (in general) with some piece of matter! Neutrinos are a very efficient carrier of energy drain from optically thick objects and they can serve as very good probes for studying the interior of such objects. Neutrino astronomy is just being born in recent years. IceCube and future neutrino “telescopes” will be able to see the Universe in a range of wavelengths and frequencies we have not ever seen till now. Electromagnetic radiation becomes “opaque” at some very high energies that neutrinos are likely been able to explore! Isn’t it wonderful? Neutrinos are high energy “telescopes”!
By the other hand, the solar neutrino flux is, together with heliosysmology and the field of geoneutrinos (neutrinos coming from the inner shells of Earth), some of the known probes of solar core and the Earth core. A similar statement applies to objects like type-II supernovae. Indeed, the most interesting questions around supernovae and the explosion dynamics itself with the shock revival (and the synthesis of the heaviest elements by the so-called r-processes) could be positively affected by changes in the observed neutrino fluxes (via some processes called resonant conversion, and active-sterile conversions).
Finally, ultra high energy neutrinos are likely to be useful probes of diverse distant astrophysical objects. Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) should be copious emitters of neutrinos, providing detectable point sources and and observable “diffuse” background which is larger in fact that the atmospheric neutrino background in the very high energy range. Relic cosmic neutrinos, their thermal background, known as the cosmic neutrino background, and their detection about 1.9K are one of the most important lacking missing pieces in the Standard Cosmological Model (LCDM).
Do you understand why neutrinos are my favorite particles? I will devote this basic thread to them. I will make some advanced topics in the future. I promise.
May the Neutrinos be with you!
Posted: 2013/05/26 | Author: amarashiki | Filed under: Cosmology, General Relativity, Physmatics | Tags: astrophysical measurements, baryons, closed universe, CMB, CNB, cosmological constant, cosmological measurements, critical density, dark energy, dark matter, density parameters, dust, evolution, evolution of the Universe, flat universe, Hubble radius, Hubble time, massive neutrinos, massless neutrinos, matter density, MD universe, MOG, MOND, neutrinos, open universe, particle species, photons, radiation density, RD universe, relic neutrinos, relic photons, scale factor, total density, vacuum energy, VD universe |



Evolution of the Universe: the scale factor
The Universe expands, and its expansion rate is given by the Hubble parameter (not constant in general!)

Remark (I): The Hubble “parameter” is “constant” at the present value (or a given time/cosmological age), i.e.,  .
.
Remark (II): The Hubble time defines a Hubble length about  , and it defines the time scale of the Universe and its expasion “rate”.
, and it defines the time scale of the Universe and its expasion “rate”.
The critical density of matter is a vital quantity as well:

We can also define the density parameters

This quantity represents the amount of substance for certain particle species. The total composition of the Universe is the total density, or equivalently, the sum over all particle species of the density parameters, that is:

There is a nice correspondence between the sign of the curvature  and that of
and that of  . Using the Friedmann’s equation
. Using the Friedmann’s equation

then we have

Thus, we observe that
1st.  if and only if (iff)
if and only if (iff)  , i.e., iff the Universe is spatially closed (spherical/elliptical geometry).
, i.e., iff the Universe is spatially closed (spherical/elliptical geometry).
2nd.  if and only if (iff)
if and only if (iff)  , i.e., iff the Universe is spatially “flat” (euclidean geometry).
, i.e., iff the Universe is spatially “flat” (euclidean geometry).
3rd.  if and only if (iff)
if and only if (iff)  , i.e., iff the Universe is spatially “open” (hyperbolic geometry).
, i.e., iff the Universe is spatially “open” (hyperbolic geometry).
In the early Universe, the curvature term is negligible (as far as we know). The reason is as follows:
 as
as  goes to zero. MD means matter dominated Universe, and RD means radiation dominated Universe. Then, the Friedmann’s equation at the early time is given by
goes to zero. MD means matter dominated Universe, and RD means radiation dominated Universe. Then, the Friedmann’s equation at the early time is given by

Furthermore, the evolution of the curvature term

is given by

and thus

The spatial curvature will be given by

and the curvature radius will be

We have arrived at the interesting result that in the early Universe, it was nearly “critical”. The Universe close to the critical density is very flat!
By the other hand, supposing that  , we can integrate the Friedmann’s equation easily:
, we can integrate the Friedmann’s equation easily:

Then, we obtain
![\dot{a}^2=H_0^2\left[-\Omega_k+\sum_i\Omega_ia^{-1-3\omega_i}\right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cdot%7Ba%7D%5E2%3DH_0%5E2%5Cleft%5B-%5COmega_k%2B%5Csum_i%5COmega_ia%5E%7B-1-3%5Comega_i%7D%5Cright%5D&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
We can make an analogy of this equation to certain simple equation from “newtonian Mechanics”:

Therefore, if we identify terms, we get that the density parameters work as “potential”, with
![\displaystyle{V(a)=\dfrac{1}{2}H_0^2\left[\Omega_k-\sum_i\Omega_ia^{-1-3\omega_i}\right]}](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cdisplaystyle%7BV%28a%29%3D%5Cdfrac%7B1%7D%7B2%7DH_0%5E2%5Cleft%5B%5COmega_k-%5Csum_i%5COmega_ia%5E%7B-1-3%5Comega_i%7D%5Cright%5D%7D&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
and the total energy is equal to zero (a “machian” behaviour indeed!). In addition to this equation, we also get
![\boxed{\displaystyle{H_0t=\int_0^a\left[-\Omega_k+\sum_i\Omega_i\chi^{-1-3\omega_i}\right]^{-1/2}d\chi}}](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cboxed%7B%5Cdisplaystyle%7BH_0t%3D%5Cint_0%5Ea%5Cleft%5B-%5COmega_k%2B%5Csum_i%5COmega_i%5Cchi%5E%7B-1-3%5Comega_i%7D%5Cright%5D%5E%7B-1%2F2%7Dd%5Cchi%7D%7D&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
The age of the Universe can be easily calculated (symbolically and algebraically):

with
![f(\Omega_i)=\int_0^1\left[-\Omega_k+\sum_i\Omega_i\chi^{-1-3\omega_i}\right]^{-1/2}d\chi](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=f%28%5COmega_i%29%3D%5Cint_0%5E1%5Cleft%5B-%5COmega_k%2B%5Csum_i%5COmega_i%5Cchi%5E%7B-1-3%5Comega_i%7D%5Cright%5D%5E%7B-1%2F2%7Dd%5Cchi&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
This equation can be evaluated for some general and special cases. If we write  for a single component, then
for a single component, then
 if
if 
Moreover, 3 common cases arise:
1) Matter dominated Universe (MD): 
2) Radiation dominated Universe (RD): 
3) Vacuum dominated Universe (VD):  (
( for the cosmological constant, vacuum energy or dark energy).
for the cosmological constant, vacuum energy or dark energy).
THE MATTER CONTENT OF THE UNIVERSE
We can find out how much energy is contributed by the different compoents of the Universe, i.e., by the different density parameters.
Case 1. Photons.
The CMB temperature gives us “photons” with 
The associated energy density is given by the Planck law of the blackbody, that is
 and
and 
or equivalently

Case 2. Baryons.
There are four established ways of measuring the baryon density:
i) Baryons in galaxies: 
ii) Baryons through the spectra fo distant quasars: 
iii) CMB anisotropies: 
iv) Big Bag Nucleosynthesis: 
Note that these results are “globally” compatible!
Case 3. (Dark) Matter/Dust.
The mass-to-light ratio from galactic rotation curves are “flat” after some cut-off is passed. It also works for clusters and other bigger structures. This M/L ratio provides a value about  . Moreover, the galaxy power spectrum is sensitive to
. Moreover, the galaxy power spectrum is sensitive to  . It also gives
. It also gives  . By the other hand, the cosmic velocity field of galaxies allows us to derive
. By the other hand, the cosmic velocity field of galaxies allows us to derive  as well. Finally, the CMB anisotropies give us the puzzling values:
as well. Finally, the CMB anisotropies give us the puzzling values:


We are forced to accept that either our cosmological and gravitational theory is a bluff or it is flawed or the main component of “matter” is not of baryonic nature, it does not radiate electromagnetic radiation AND that the Standard Model of Particle Physics has no particle candidate (matter field) to fit into that non-baryonic dark matter. However, it could be partially formed by neutrinos, but we already know that it can NOT be fully formed by neutrinos (hot dark matter). What is dark matter? We don’t know. Some candidates from beyond standard model physics: axion, new (likely massive or sterile) neutrinos, supersymmetric particles (the lightest supersymmetric particle LSP is known to be stable: the gravitino, the zino, the neutralino,…), ELKO particles, continuous spin particles, unparticles, preons, new massive gauge bosons, or something even stranger than all this and we have not thought yet! Of course, you could modify gravity at large scales to erase the need of dark matter, but it seems it is not easy at all to guess a working Modified Gravitational theory or Modified Newtonian(Einsteinian) dynmanics that avoids the need for dark matter. MOND’s, MOG’s or similar ideas are an interesting idea, but it is not thought to be the “optimal” solution at current time. Maybe gravitons and quantum gravity could be in the air of the dark issues? We don’t know…
Case 4. Neutrinos.
They are NOT observed, but we understand them their physics, at least in the Standard Model and the electroweak sector. We also know they suffer “oscillations”/flavor oscillations (as kaons). The (cosmic) neutrino temperature can be determined and related to the CMB temperature. The idea is simple: the neutrino decoupling in the early Universe implied an electron-positron annihilation! And thus, the (density) entropy dump to the photons, but not to neutrinos. It causes a difference between the neutrino and photon temperature “today”. Please, note than we are talking about “relic” neutrinos and photons from the Big Bang! The (density) entropy before annihilation was:
![s(a_1)=\dfrac{2\pi^2}{45}T_1^3\left[2+\dfrac{7}{8}(2\cdot 2+3\cdot 2)\right]=\dfrac{43}{90}\pi^2 T_1^3](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=s%28a_1%29%3D%5Cdfrac%7B2%5Cpi%5E2%7D%7B45%7DT_1%5E3%5Cleft%5B2%2B%5Cdfrac%7B7%7D%7B8%7D%282%5Ccdot+2%2B3%5Ccdot+2%29%5Cright%5D%3D%5Cdfrac%7B43%7D%7B90%7D%5Cpi%5E2+T_1%5E3&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
After the annihilation, we get
![s(a_2)=\dfrac{2\pi^2}{45}\left[2T_\gamma^3+\dfrac{7}{8}(3\cdot 2)T_\nu^3\right]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=s%28a_2%29%3D%5Cdfrac%7B2%5Cpi%5E2%7D%7B45%7D%5Cleft%5B2T_%5Cgamma%5E3%2B%5Cdfrac%7B7%7D%7B8%7D%283%5Ccdot+2%29T_%5Cnu%5E3%5Cright%5D&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
Therefore, equating
 and
and 
)^3](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cdfrac%7B43%7D%7B90%7D%5Cpi%5E2%28a_1T_1%29%5E3%3D%5Cdfrac%7B2%5Cpi%5E2%7D%7B45%7D%5Cleft%5B2%5Cleft%28%5Cdfrac%7BT_%5Cgamma%7D%7BT_%5Cnu%7D%5Cright%29%5E3%2B%5Cdfrac%7B42%7D%7B8%7D%5Cright%5D%28a_2T_%5Cnu+%28a_2%29%29%5E3&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
)^3](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cdfrac%7B43%7D%7B2%7D%5Cpi%5E2%28a_1T_1%29%5E3%3D2%5Cpi%5E2%5Cleft%5B2%5Cleft%28%5Cdfrac%7BT_%5Cgamma%7D%7BT_%5Cnu%7D%5Cright%29%5E3%2B%5Cdfrac%7B42%7D%7B8%7D%5Cright%5D%28a_2T_%5Cnu+%28a_2%29%29%5E3&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
and then

or equivalently
![\boxed{T_\nu=\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{4}{11}}T_\gamma\approx 1\mbox{.}9K}](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=%5Cboxed%7BT_%5Cnu%3D%5Csqrt%5B3%5D%7B%5Cdfrac%7B4%7D%7B11%7D%7DT_%5Cgamma%5Capprox+1%5Cmbox%7B.%7D9K%7D&bg=f9f7e1&fg=000000&s=0&c=20201002)
In fact, the neutrino energy density can be given in two different ways, depending if it is “massless” or “massive”. For massless neutrinos (or equivalently “relativistic” massless matter particles):
I) Massless neutrinos: 
2) Massive neutrinos: 
Case 5. The dark energy/Cosmological constant/Vacuum energy.
The budget of the Universe provides (from cosmological and astrophysical measurements) the shocking result
 with
with 
Then, there is some missin smooth, unclustered energy-matter “form”/”species”. It is the “dark energy”/vacuum energy/cosmological cosntant! It can be understood as a “special” pressure term in the Einstein’s equations, but one with NEGATIVE pressure! Evidence for this observation comes from luminosity-distance-redshift measurements from SNae, clusters, and the CMB spectrum! The cosmological constant/vacuum energy/dark energy dominates the Universe today, since, it seems, we live in a (positively!) accelerated Universe!!!!! What can dark energy be? It can not be a “normal” matter field. Like the Dark Matter field, we believe that (excepting perhaps the scalar Higgs field/s) the SM has no candidate to explain the Dark Energy. What field could dark matter be? Perhaps an scalar field or something totally new and “unknown” yet.
In short, we are INTO a DARKLY, darkly, UNIVERSE! Darkness is NOT coming, darkness has arrived and, if nothing changes, it will turn our local Universe even darker and darker!
See you in the next cosmological post!
) and that the young neutrino Astronomy or neutrino telescopes will become more and more important in the future. The reasons are simple:
, or about 8 joules. This Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin limit (GZK limit) is a theoretical upper limit on the energy of cosmic rays, since at some high energy, that can be computed, they would interact with the CMB photons producing a delta particle (
) which would spoil the observed cosmic rays flux as its decays would not be detected after “a long trip”. Then, it can only be approached when the cosmic rays travel very long distances (hundreds of million light-years or more). Here you are a typical picture of SuperKamiokande cosmic ray detection:
if the SM is right, and their associated neutrino density now is about
per cubic centimeter per species (neutrino plus antineutrino), or
per cubic centimeter including the 3 flavors! Relic neutrinos are almost everywhere, but they are very, very feeble (neutral and weakly interacting) particles. While detecting the
temperature is one of the most challenging tests of the standard cosmological model, we can try to detect the existence of these phantom neutrinos using a similar (quantum) trick than the one used in the GZK limit (there the delta particle resonance). If some ultra high energy cosmic ray (likely a neutrino coming from some astrophysical source) hits a “relic neutrino” with energy high enough to produce, say, a Z boson (neutral particle as the neutrino himself), then we should observe a “dip” in the cosmic ray spectrum corresponding to this “Z-burst” event! This mechanism is also called the ZeVatron or the Z-dip. It also shows the deep links between particle physics and Cosmology or Astrophysics. When an ultra-high energy cosmic neutrino collides with a relic anti-neutrino in our galaxy and annihilates to hadrons, this process proceeds via a (virtual) Z-boson:
) the formulae:

 Neutrino oscillations are a purely quantum effect, and thus, they open a really interesting “new channel” in which we can observe the whole Universe. Yes, neutrinos are cool!!! The coolest particles in all over the world! We can not imagine yet what neutrino will show and teach us about the current, past and future of the cosmological evolution.
Neutrino oscillations are a purely quantum effect, and thus, they open a really interesting “new channel” in which we can observe the whole Universe. Yes, neutrinos are cool!!! The coolest particles in all over the world! We can not imagine yet what neutrino will show and teach us about the current, past and future of the cosmological evolution.). Anyway, this line is controversial and its presence has yet to be proved with enough statistical confidence (5 sigmas are usually required in the particle physics community). Of course, the issue with this resonant hypothesis would be that we should expect that this particle would decay into hadrons leaving some indirect clues of those events. The Fermi line can indeed have more explanations and/or be a fluke in the data due to a bad modeling or a bad substraction of the background. Time will tell us if the Fermi line is really here as well.
) make a contribution to the total energy density of the Universe given by:
for Dirac (Majorana) neutrinos in the framework of the Standard Model. The number density of the neutrino sea is revealed to be related to the photon number density by entropy conservation (entropy conservation is the key of this important cosmological result!) in the adiabatic expansion of the Universe:
and the cosmic microwave background (CMB):
temperature should be about
and the quantity of neutrino “hot dark matter” present in the Universe!
is related to the total neutrino density and the critical density as follows:
, and then we get
the reduced Hubble constant. Recent analysis provide
(PLANCK/WMAP).
is the total mass density of the Universe as a fraction of the critical density
. This
includes radiation (photons), bayrons and non-baryonic “cold dark matter” (CDM) and “hot dark matter” (HDM). The two first components in the decomposition of
. In the SM framework, the only HDM component are the neutrinos!
does not exceed even
. Requiring that
, we get that
. Using the relationship with the total mass density, we can deduce that the total neutrino mass (or HDM in the SM) is about
or less!
or higher) can also be obtained along the same reasoning. The puzzle gets very different if the neutrinos were “unstable” particles. One gets then joint bounds on mass and timelife, and from them, we deduce limits that can overcome the previously seen limits (above).
, the reader can easily check that
. This is the Tremaine-Gunn bound. It is based on the idea that neutrinos form an important part of the galactic bulges and it uses the phase-space restriction from the Fermi-Dirac distribution to get the lower limit on the neutrino mass. I urge you to consult the literature or google to gather more information about this tool and its reliability.
, the uncertainty in the halo core radius (interior to which the mass density saturates) limits the reliability of this neutrino mass bound. However, some authors take it seriously! As Feynman used to say, everything depends on the prejudges you have!
or additional relativistic degrees of freedom uncharged under the Standard Model can change the number of relativistic degrees of freedom
. Sometimes you will hear about the number
. Planck data, recently released, have decreased the hopes than we would be finding some additional relativistic degree of freedom that could mimic neutrinos. It is also constrained by the BBN and the deuterium abundances we measured from astrophysical objects. Any sterile neutrino or extra relativistic degree of freedom would enter into equilibrium with the active neutrinos via neutrino oscillations! A limit on the mass differences and mixing angle with another active neutrino of the type
should be accomplished in principle. From here, it can be deduced that the effective number of neutrino species allowed by neutrino oscillations is in fact a litle higher the the 3 light neutrinos we know from the Z-width bound:
. However, systematical uncertainties in the derivation of the BBN make it too unreliable to be taken too seriously and it can eventually be avoided with care.






















You must be logged in to post a comment.